AI vs. Google Search: When to Ask Questions and When to Search
- Sindu Mohan
- Dec 4, 2025
- 3 min read
In this digital age, we have two incredibly powerful tools at our fingertips for finding information: traditional search engines like Google and the new wave of Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT, Bard, or Claude. Both are excellent for information retrieval, but they operate on different principles and excel at different types of tasks.
Understanding when to "ask" an AI and when to "search" on Google can significantly improve your efficiency and the quality of the information you get.
The Core Difference: Retrieval vs. Generation
At a fundamental level, here's the distinction:
Google Search (and other search engines): Primarily a retrieval system. It's designed to index the vastness of the internet and find existing web pages that match your keywords. It connects you to sources.
AI Chatbots (Large Language Models - LLMs): Primarily a generative system. While they have access to an enormous dataset of information (often derived from the internet), they generate new text based on patterns learned from that data. They synthesize information.
When to "Search" on Google: Your Go-To for Factual, Verifiable, and Source-Dependent Information
Think of Google as your librarian for the entire internet.
Breaking News & Real-Time Events: For the very latest updates on current events, sports scores, stock prices, or anything that changes rapidly, Google is superior. It pulls information directly from constantly updated websites.
Example: "What's the score of the Lakers game right now?"
Example: "Latest news on the recent earthquake in Japan."
Verifiable Facts & Citations: When you absolutely need to know the source of information, double-check facts, or require links to original research papers, articles, or official websites. Google gives you a list of sources to scrutinize.
Example: "Population of Denmark 2023 source" (You'll get official census sites).
Example: "Studies on the effectiveness of creatine for muscle growth PubMed"
Shopping & Product Information: For finding specific products, comparing prices, reading reviews, or locating e-commerce sites, Google is designed for this.
Example: "Best noise-canceling headphones reviews"
Example: "Buy ergonomic office chair near me"
Local Information & Navigation: Directions, business hours, restaurant menus, local services – Google Maps and Google Search are integrated to provide this.
Example: "Coffee shops open late near me"
Example: "Pharmacy in downtown Anycity hours"
Troubleshooting Specific Error Messages/Codes: When you encounter a very specific error code from software or hardware, pasting it directly into Google is often the fastest way to find forum discussions, official support pages, and solutions.
Example: "Error 0x80070005 Windows Update"
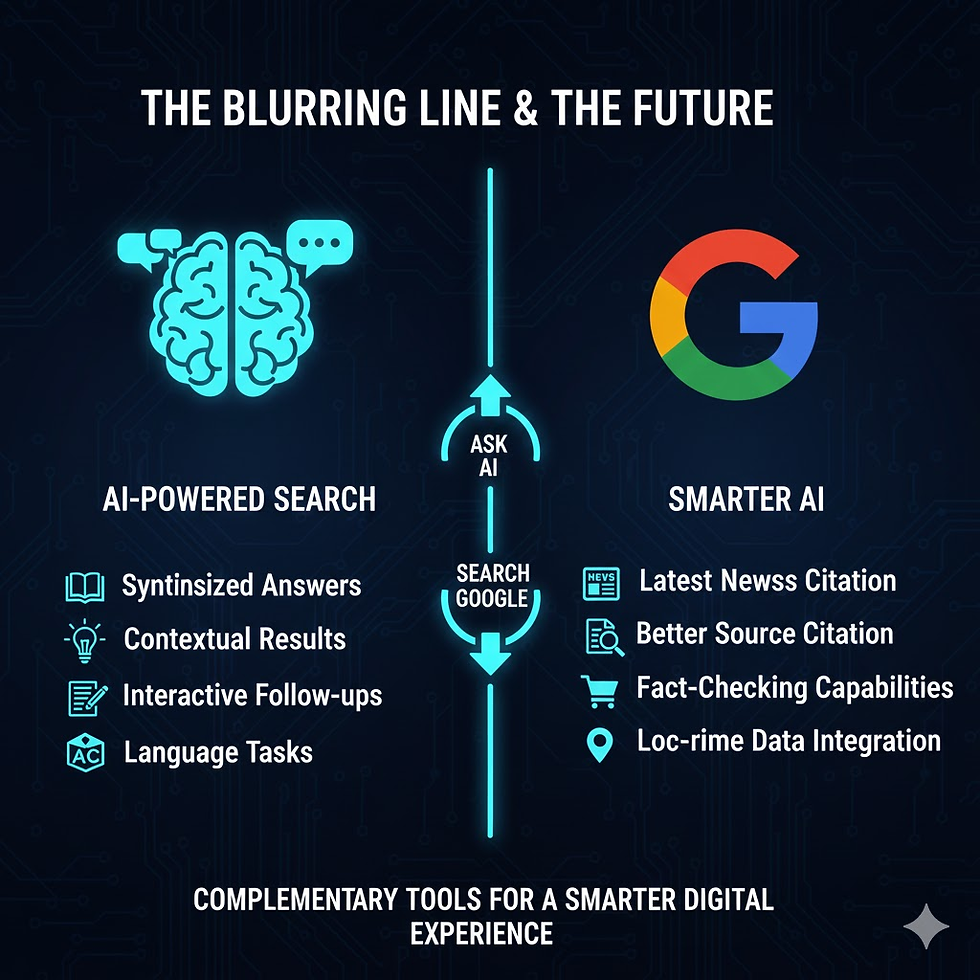
When to "Ask" an AI: Your Creative Assistant, Explainer, and Brainstorming Partner
Think of an AI chatbot as a knowledgeable, articulate assistant who can synthesize, summarize, and generate.
Explanations & Simplification: When you need a complex topic broken down into simpler terms, explained from a different perspective, or tailored to a specific audience.
Example: "Explain quantum entanglement to a 10-year-old."
Example: "What are the pros and cons of socialism?"
Brainstorming & Idea Generation: For creative tasks, generating lists of ideas, titles, outlines, or different angles for a project.
Example: "Give me 10 ideas for a fantasy novel plot."
Example: "Suggest catchy slogans for a new eco-friendly cleaning product."
Summarisation & Synthesis: To condense long articles, papers, or conversations, or to combine information from multiple perspectives into a coherent summary.
Example: "Summarize the key arguments of Kant's 'Critique of Pure Reason'."
Example: "What are the main differences between Impressionism and Expressionism?"
Drafting & Content Creation: For generating emails, blog posts, social media captions, code snippets, or even creative writing.
Example: "Write a polite email requesting a meeting with a busy executive."
Example: "Generate a Python function to reverse a string."
Language Tasks: Translation, grammar correction, rephrasing sentences, or expanding on a thought.
Example: "Rewrite this paragraph to be more formal."
Example: "Translate 'Hello, how are you?' into French."
Simulated Conversations & Role-Playing: For practicing interviews, getting feedback on ideas, or exploring hypothetical scenarios.
Example: "Act as a tough interviewer for a software engineer role."
Example: "What would happen if the moon disappeared?"

The Blurring Lines and the Future
It's important to note that the line between AI and Search is rapidly blurring. Google is integrating AI into its search results (SGE - Search Generative Experience), and AI models are getting better at citing their sources. However, the core distinction in their primary function remains.
Conclusion
Neither AI nor Google Search is inherently "better" than the other; they are complementary tools.
When you need to know where the information came from, how current it is, or need to verify specific facts, stick with Google Search.
When you need to understand, create, summarize, or brainstorm, turn to an AI chatbot.
By choosing the right tool for the job, you'll harness the full potential of both AI and traditional search, becoming a more effective and informed digital citizen.





Comments