Understanding the Different Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Sindu Mohan
- Jan 8
- 2 min read
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way businesses operate, learn, and innovate. While AI is often discussed as a single concept, it actually exists in different forms, each with distinct capabilities and limitations.
Understanding these differences is essential for organisations and individuals to use AI effectively, ethically, and realistically. This blog breaks down the main types of AI in a clear and structured way.
1. Types of AI Based on Capability
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)

This is the most common and widely used form of AI today.
What it does:
Performs a specific task efficiently
Operates within a defined scope
Examples:
Chatbots and virtual assistants
Recommendation systems
Navigation and route optimization tools
Key takeaway: ANI is powerful but task-specific. It does not think or reason beyond its programmed function.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)

AGI refers to AI that can understand, learn, and apply intelligence across multiple tasks—similar to humans.
Current status:
Still under research
Not available in real-world applications
Key takeaway:AGI represents the future vision of AI, not current reality.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)

ASI is a theoretical concept where AI surpasses human intelligence in every domain.
Current status:
Exists only in theory and science fiction
Key takeaway:ASI raises important ethical discussions but is not part of today’s AI landscape.
2. Types of AI Based on Functionality

Reactive Machines
Respond only to current inputs
Do not learn from past experiences
Example:Rule-based systems and early game-playing computers.
Limited Memory AI
Learns from historical data
Improves decision-making over time
Examples:
Recommendation engines
Fraud detection systems
Logistics and supply chain optimization tools
Key takeaway:Most modern AI systems fall under this category.
Theory of Mind AI
Designed to understand human emotions and intentions
Still in research and experimentation stages
Self-Aware AI
Hypothetical AI with self-awareness
No real-world implementation
3. Rule-Based AI vs Data-Driven AI
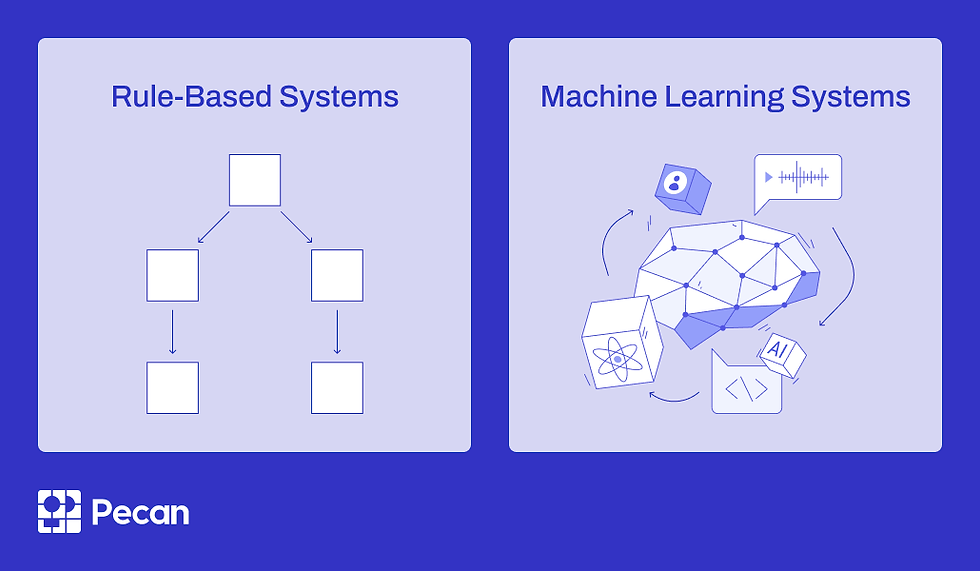
Rule-Based AI
Operates on predefined rules
Predictable and consistent
Limited flexibility
Best suited for:Simple, well-defined processes.
Data-Driven AI
Learns patterns from data
Adapts and improves over time
Handles complex scenarios
Best suited for:Dynamic environments and large-scale decision-making.
Why Understanding AI Types Matters
For organizations, knowing the right type of AI to use helps:
Set realistic expectations
Avoid over-dependence on automation
Build responsible AI strategies
Empower humans rather than replace them
AI today is a powerful assistant—not a replacement for human judgment, creativity, or empathy.
Conclusion
AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution. From narrow task-focused systems to advanced learning models, each type of AI serves a specific purpose. By understanding these differences, organisations can adopt AI thoughtfully, responsibly, and effectively.
At its best, AI enhances human potential—and that is where its true value lies.





Comments